FTPS requirements for x360Recover vaults
FTPS services on your vault are intended to operate in FTP passive mode.
- For clients to connect to the service, standard FTP ports 20 and 21 should be port-forwarded to the vault and should be opened to the internet.
- The PASV port range (for passive mode operation), has been configured to use ports 10000-11024 for client data communications. This port range must also be port-forwarded to the vault and open to the Internet.
What is the Difference Between FTP, FTPS, and SFTP?
|
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is unsecured. This means FTP connections, data, authentication and other communications between the client and the server are sent unencrypted, in plain text. Being unsecured in this way is not a good practice. x360Recover does not allow unencrypted FTP connections. |
|
FTPS is secured FTPS leverages the same public key infrastructure and X.509 security certificates as HTTPS to secure your connections. FTPS certificates are typically signed by a trusted certificate authority and provide for trusted identity management. Both control and data sessions are encrypted using SSL or TLS with signed, trusted public keys provided by the server. x360Recover supports FTPS. |
|
SFTP is not related to either FTP or FTPS SFTP is a totally separate file transfer protocol, not related to FTP/FTPS at all. SFTP operates over an ssh tunnel established on port 22. SFTP also utilizes ssh keys to encrypt and secure communications. Unlike x.509 PKI certificates, ssh keys do not validate the integrity of the certificate or the authenticity of the owner. SFTP is typically substantially slower than FTPS. x360Recover does not support SFTP. |
How does FTP/FTPS Work?
Active mode
- In active mode, the client connects to the FTP server on port 21 to issue control and command operations to the server.
- The server then connects back to the client on port 20 for data transfer operations.
- For this to work, the client must be directly accessible on the internet on port 20 (and this is almost never the case in the modern internet world.)
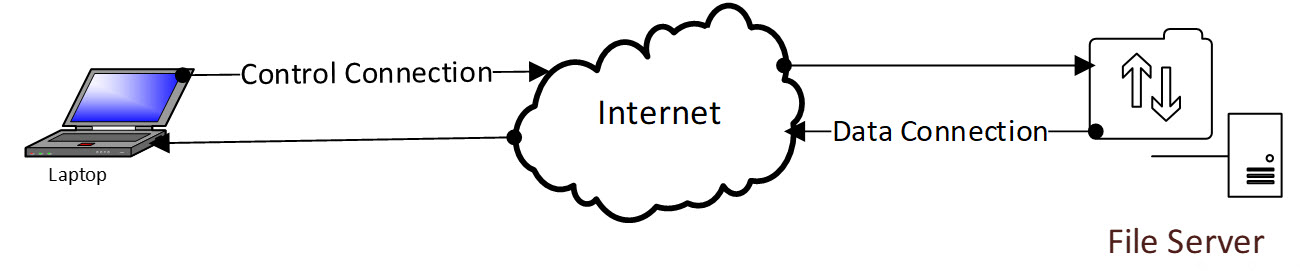
Passive mode
- In passive mode, the client still connects to the server on port 21 for control operations.
- When file transfers are to occur, the server requests that the client make a data connection on an available PASV port.
- In this way, only the server needs to be directly accessible on the internet.

FTPS services on x360Recover vaults are intended to operate in FTP passive mode.
Why are so many PASV ports required?
Control session on port 21 utilizes a standard daemonized TCP service.
This means that the initial connection on the public port is automatically transferred to another session port, allowing the service to support multiple users on a single public connection port address.
PASV connections are not daemonized. Each port connection is dedicated to a single client session.
FTP supports the use of multiple data connections to accelerate transmission of many files and folders. This explains why a single user session may consume many data transfer ports. To facilitate multiple simultaneous users, each with multiple data connections, a large range of PASV ports was provisioned for the service.
SUPPORT | 720-204-4500 | 800-352-0248
- Contact Axcient Support at https://partner.axcient.com/login or call 800-352-0248
- Free certification courses are available in the Axcient x360Portal under Training
- Subscribe to the Axcient Status page for a list of updates and scheduled maintenance
865