Overview
xCloud Agent for Linux relies upon a custom kernel driver module for capturing a snapshot of the live filesystem for backups.
Linux does not have a native filesystem snapshot system (like the Volume Shadow copy Service (VSS) within Windows), so we have to inject our own custom driver service to enable this functionality.
- Due to the nature of kernel-level drivers within Linux, the kernel module (elastio-snap) must be compiled to match the exact build of the Linux kernel running on the system. As it would be impossible to pre-compile modules ahead of time for all possible kernel releases, Linux uses the Dynamic Kernel Module Service (DKMS) to automate the process of compiling custom driver modules against the running kernel whenever a new kernel update is installed.
UEFI Secure Boot is a hardware-level security system designed to prevent malicious code from being run during the boot-up of a system. UEFI Secure Boot examines the binary applications being launched by the system loader and validates that they are signed by a trusted certificate to ensure security.
- The motherboard of your UEFI system comes pre-loaded with the digital signatures of broadly trusted certificate providers (like Microsoft)
- Mainstream Linux distribution providers (like Debian, Red Hat, and Ubuntu) also utilize trusted certificates widely recognized by hardware manufacturers
However, the custom built DKMS modules installed by third party developers (like Axcient) cannot be signed by these well-known certificates.
To enable the xCloud Agent for Linux to install and operate properly on a UEFI system using UEFI Secure Boot, you must first generate and enroll a custom certificate for the driver to utilize during installation.
By design, this process requires a user with root-level access on the specific system to manually perform an enrollment process. This process cannot be automated (or it would defeat the underlying security layer being provided by UEFI Secure Boot.)
Below are instructions for performing this process.
IMPORTANT NOTE #1: Perform the following steps BEFORE installing the Agent for Linux.
IMPORTANT NOTE #2: UEFI Secure Boot is relevant ONLY for systems booting in UEFI mode. Do not perform this configuration for systems booting in Legacy BIOS mode.
STEP 1. Install the prerequisite packages
Before you can generate a signing certificate and enroll the security key in the system BIOS, you must first install the prerequisite packages on your Linux system.
1.1. First, login to your Linux system and switch to the root user account.
For Debian and Ubuntu-based Linux distributions, run:
“apt install -y mokutil dkms openssl”
For Red Hat-based Linux systems, you must first install and enable the EPEL repository.
For details in installing EPEL, see the documentation: Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL)
Once EPEL is enabled, run the following to install the required packages
“yum install -y mokutil dkms openssl”
STEP 2. Generate the signing certificate
2.1. Once you have installed the prerequisite packages, verify that the default signing certificate has been created.
For Debian and Ubuntu, the default signing file is MOK.der and should be present in /var/lib/shim-signed/mok.
For RHEL and CentOS, the default signing file is mok.pub and may or may not be present in /var/lib/dkms, depending on the RHEL release version.
2.2. If this file is not present, you can create it manually.
From a shell or terminal login run the following command to generate the signing certificate:
For Debian and Ubuntu
openssl req -new -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /var/lib/shim-signed/mok/MOK.priv -outform DER -out /var/lib/shim-signed/mok/MOK.der -nodes -days 36500 -subj "/CN=Axcient Driver Kmod Signing MOK"
For RHEL and CentOS
openssl req -new -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /var/lib/dkms/mok.priv -outform DER -out /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub -nodes -days 36500 -subj "/CN=Axcient Driver Kmod Signing MOK"
This will generate the private and public key pair in the default folder where DKMS expects to find it. Whenever a new kernel version is installed or updated, these keys are required to be present to allow DKMS to rebuild and sign a new kernel module for the elastio-snap driver service.
Note: Make sure you complete the Certificate Enrollment step below so that the system will trust this certificate for signing.
STEP 3. Enroll the certificate on the system
The following process will (a) install the new certificate on the system and (b) allow the motherboard and UEFI Secure Boot mechanism to trust binaries signed with this certificate.
3.1. To begin the enrollment process, run the following command as the root user from the system console:
For Debian and Ubuntu
mokutil --import /var/lib/shim-signed/mok/MOK.der
For RHEL and CentOS
mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub
3.2. You will be prompted to create a password.
Once completed, the enrollment has been queued.
3.3. To continue, reboot the machine.
Note: You must have access to the physical console of the system, either using (a) the virtual machine console utility, (b) the physical keyboard and monitor, or (c) the IPMI KVM utility. You cannot perform enrollment via remote shell connections.
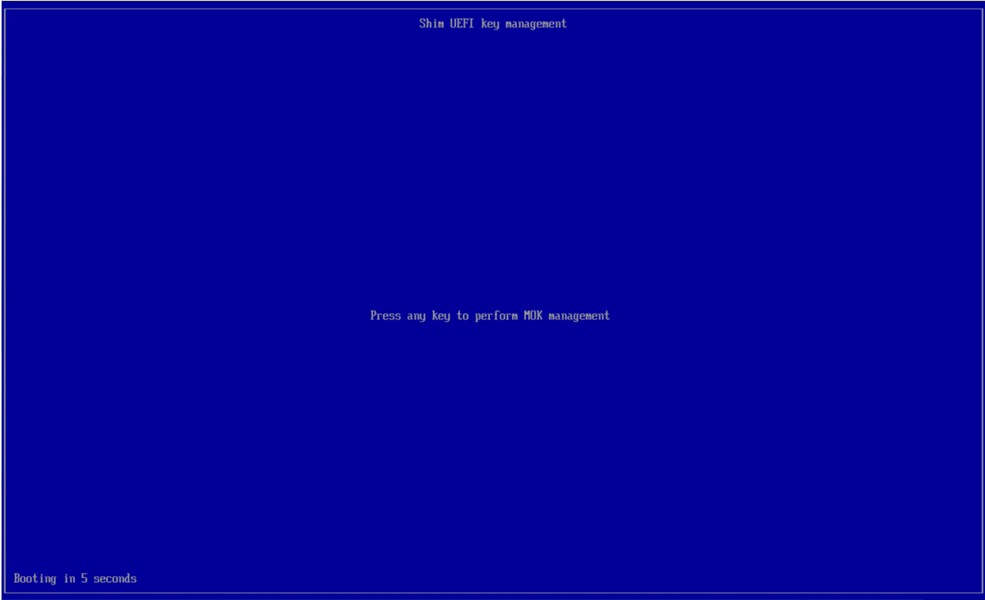
3.4. After running the mokutil command above to initiate the enrollment process, reboot the system. When the machine reboots, the MOK Management system should appear with a Press any key message to continue.
IMPORTANT: You have only 10 seconds to press a key or the system will continue with normal startup and skip the enrollment process. You will need to run mokutil and reboot again to retry.
After pressing a key, the enrollment process will begin
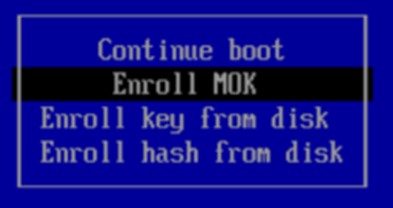
3.5. Select Enroll MOK and press Continue.
3.5.1. On the next page, select Continue
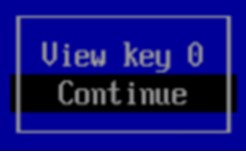
3.5.2. Next, select Yes

3.6. Enter the password you created above when prompted.

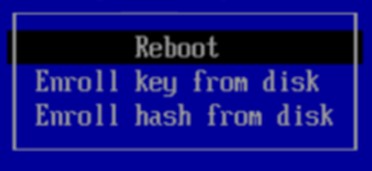
3.7. Enrollment is complete.
Select Reboot to continue.
The private Machine Owner Key (MOK) certificate present on this system is now trusted by the BIOS for signing of binary executable files.
STEP 4. Continue with the agent for Linux installation
4.1. Once the signing certificate has been enrolled, continue with installation of the agent for Linux as usual.
The installer will
- detect that the system is running using UEFI Secure Boot
- detect that the signing certificate is present and
- configure the DKMS driver to automatically build signed binaries using the certificate
Troubleshooting
Debian 11
On Debian 11, it was reported that some manual configuration of DKMS signing is required.
1. Edit the file /etc/dkms/sign_helper.sh and add the following line:
/lib/modules/"$1"/build/scripts/sign-file sha512 /var/lib/shim-signed/mok/MOK.priv /var/lib/shim-signed/mok/MOK.der "$2"
2. Edit the file /etc/dkms/framework.conf and uncomment the sign_tool helper option:
## Script to sign modules during build, script is called with kernel version
## and module name
sign_tool="/etc/dkms/sign_helper.sh"
Debian 12
On Debian 12, DKMS module signing is preconfigured. You don’t need to modify any configuration files but the Debian installer does not automatically enroll the Machine Owner Key (MOK) like Ubuntu does. You have to manually enroll the mok file.
BEFORE INSTALLING THE AGENT, perform the following steps:
1. Login to the system and open a terminal session (aka Konsole.)
2. Elevate to root user by running ‘su –‘
Note that the dash is important. Without it the root user session will not have the correct path assignment.
3. Stage the enrollment by running ‘mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pub’
4. You will be required to enter a password, then re-enter it again for confirmation.
5. Reboot the system.
6. On reboot. you will be presented with a bootloader screen. Press a key to begin the MOK enrollment process.
7. Proceed through the options to enroll the mok key.
8. Enter the password you created in the step above.
9. Select reboot once finished.
SUPPORT | 720-204-4500 | 800-352-0248
- Contact Axcient Support at https://partner.axcient.com/login or call 800-352-0248
- Have you tried our Support chat for quick questions?
- Free certification courses are available in the Axcient x360Portal under Training
- Subscribe to Axcient Status page for updates and scheduled maintenance
1717 | 1828